Solar System Reference Data
 Table of asteroids
Table of asteroids
 Table of comets
Table of comets
 Table of moons
Table of moons
 Table of planets and dwarf planets
Table of planets and dwarf planets
 Mercury,
Venus,
Earth,
Mars,
Jupiter,
Saturn,
Uranus,
Neptune (individual planet statistics pages...)
Mercury,
Venus,
Earth,
Mars,
Jupiter,
Saturn,
Uranus,
Neptune (individual planet statistics pages...)
 Pluto,
Makemake,
Ceres, Eris (individual dwarf planet statistics pages...)
Pluto,
Makemake,
Ceres, Eris (individual dwarf planet statistics pages...)
 Table of orbital data for planets and dwarf planets
Table of orbital data for planets and dwarf planets
You might also be interested in:

How did life evolve on Earth? The answer to this question can help us understand our past and prepare for our future. Although evolution provides credible and reliable answers, polls show that many people turn away from science, seeking other explanations with which they are more comfortable.
...more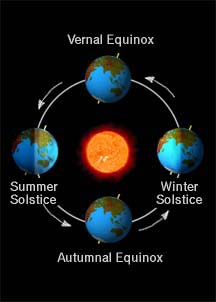
Axis tilt occurs when a planet’s rotational axis is tilted relative to the plane of its revolution around a larger object. Put simply, that means that the “top” of the planet, as defined by its rotation,
...more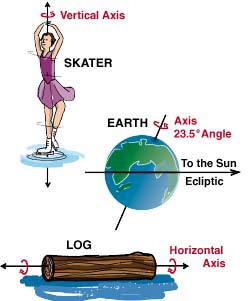
Rotational period is the term describing the length of time necessary for a space object to make one complete rotation. This time varies from planet to planet, and on Earth it is 1 day. This length of
...more
Asteroids are small bodies that are believed to be left over from the beginning of the solar system 4.6 billion years ago. They are rocky objects with round or irregular shapes up to several hundred km
...more
When we look at images of many of the planets, we see all sorts of circular craters on the planet surfaces. Most of these craters were probably formed when the solar system was still very young. Once
...more
 Table of asteroids
Table of asteroids
 Table of planets and dwarf planets
Table of planets and dwarf planets Mercury,
Venus,
Earth,
Mars,
Jupiter,
Saturn,
Uranus,
Neptune (individual planet statistics pages...)
Mercury,
Venus,
Earth,
Mars,
Jupiter,
Saturn,
Uranus,
Neptune (individual planet statistics pages...)
 Pluto,
Makemake,
Ceres, Eris (individual dwarf planet statistics pages...)
Pluto,
Makemake,
Ceres, Eris (individual dwarf planet statistics pages...) Table of orbital data for planets and dwarf planets
Table of orbital data for planets and dwarf planets










