The Ulysses Mission
News story originally written on June 30, 1997
"..Come, my friends, tis not too late to seek a newer world."-Tennyson in "Ulysses" Ulysses is a space mission designed to explore the unknown region of space above the north and south poles of the Sun. Ulysses is a joint mission of the European Space Agency (ESA) and the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA)The ESA provided the spacecraft and the team that operates the spacecraft. NASA launched the spacecraft on the Shuttle Discovery in October 1990. NASA is also responsible for radio communications and data management for the overall mission.
The Ulysses spacecraft flew by Jupiter in February 1992, for the gravity assist needed to place the spacecraft into orbit around the Sun.
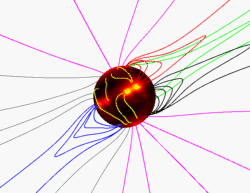
The purpose of the Ulysses mission is to investigate the solar magnetic field, solar wind plasma, and galactic cosmic rays coming from the Sun. There are 12 instruments onboard Ulysses to help scientists investigate these solar topics.
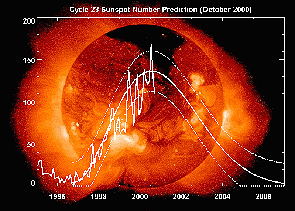
The phenomena being studied by the Ulysses mission are strongly influenced by the 11 year solar cycle. The primary mission which ended in September 1995, extended over half of the solar cycle. The secondary mission (or second pass around the Sun) happens during the second half of a cycle. It is here at solar maximum that Ulysses will encounter solar flares, coronal mass ejections and streamers.
With the first phase of its mission successfully completed, Ulysses is now in its second orbit of the Sun. This secondary phase will be finished in December 2001.