Glossary : Light
- Form of radiant energy that acts upon the retina of the eye, optic
nerve, etc., making sight possible. This energy is transmitted at a
velocity of about 186,000 miles per second by wavelike or vibrational motion.
- A form of radiant energy similar to this, but not acting on the
normal retina, such as ultraviolet and infrared radiation.
Interplay between light rays and the atmosphere cause us to see the sky
as blue, and can result in such phenomena as glows, halos, arcs, flashes,
and streamers.
Courtesy of NASA
You might also be interested in:
AU stands for Astronomical Units. It is an easy way to measure large distances in space. It is the distance between the Earth and the Sun, which is about 93 million miles. For really big distances, we
...more
The solar wind is formed as the Sun's top layer blows off into space. It carries magnetic fields still attached to the Sun. Streams appear to flow into space as if they are spiraling out from the Sun,
...more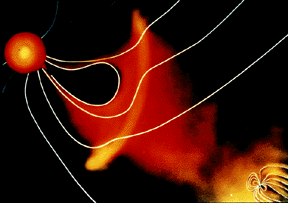
For a planet to be affected by a blob of material being ejected by the sun, the planet must be in the path of the blob, as shown in this picture. The Earth and its magnetosphere are shown in the bottom
...more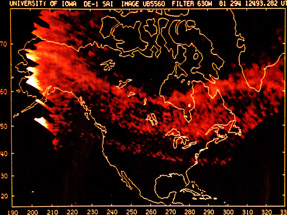
If someone says they saw an aurora, you might picture something like this. There is another type of aurora that we can't see. These aurora are called SAR arcs. The SAR stands for Stable Auroral Red. That
...more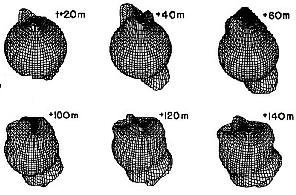
This figure shows the effect of the aurora on the atmosphere. When FAC's enter the atmosphere and create the aurora, they heat the atmosphere suddenly and abruptly. This creates an impulse which travels
...more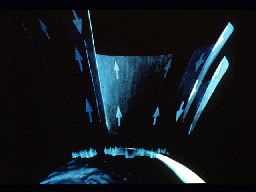
This picture shows the flowing of particles into and out of the auroral zone, as Field-Aligned currents (FAC's) take at short-cut through the atmosphere. Some of the particles entering the auroral zone
...more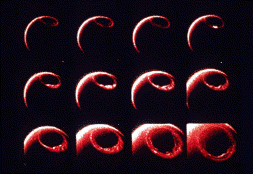
This picture shows a series of images of the auroral oval as it expands over the an hour's time because of a storm on the Sun. This is an animation of the auroral oval expanding.
...more














