The Milky Way Galaxy - Our Home

|
The Milky Way is the spiral
galaxy we call home, as do roughly 100 billion other stars. It
looks very much like other spiral galaxies when viewed from above.
There are spiral arms and a nucleus. The Sun can be found rather far
from the center of the Galaxy, halfway to the edge of visible matter
along the Orion spiral arm. The Sun is revolving at a speed of
half a million miles per hour around the center of the Galaxy, yet it
will still take 200 million years for it to go around once.
Radio observations of gas in our Galaxy reveal that the gas is feeling
the gravitational effect of matter far beyond the edge of the visible
Galaxy. Astronomers call this material dark matter, since
electromagnetic radiation from it is not currently detectable at any
wavelength.
|

A galaxy like the Milky Way as viewed from the top, and the
actual Milky Way as viewed in the infrared
Click on top image for diagram (276K JPEG)
Click on bottom image for diagram (204K JPEG)
European Southern Observatory & NASA COBE Project
|
Like other spiral galaxies, the Milky Way has a bulge, a disk, and a
halo. Although all are parts of the same galaxy, each contains
different types of objects. The central bulge contains old stars, the
halo houses globular
clusters and dark matter, and the disk is filled with gas, dust,
and young stars. Our Sun is itself a fairly young star at only 5
billion years old. The Milky Way is at least 5 billion years older
than that. The ages of globular clusters suggest that it may be
closer to 10 billion years older.
Recent observations of the numbers and distributions of stars in the
Galaxy suggest that it may have a bar!
|
 Questions and answers about the Milky Way
Questions and answers about the Milky Way
 A Matter of Scale - interactive showing the sizes of things, from very tiny to huge - from NSF
A Matter of Scale - interactive showing the sizes of things, from very tiny to huge - from NSF
You might also be interested in:

How did life evolve on Earth? The answer to this question can help us understand our past and prepare for our future. Although evolution provides credible and reliable answers, polls show that many people turn away from science, seeking other explanations with which they are more comfortable.
...more
NASA has announced its newest mission! The Far Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Explorer (FUSE) is scheduled for launch on June 23, 1999, from Cape Canaveral Air Station, FL. FUSE will be the latest satellite
...more
Bifrost, the rainbow, was the bridge leading from the Earth, called Midgard, to Asgard, the home of the gods. Only the gods could cross this bridge. Mortals and giants were prevented from reaching Asgard
...more
Cosmic rays are a type of radiation that comes from space. Cosmic rays aren't really "rays"; they are subatomic particles (mostly protons) with very high energies. Cosmic rays come from various places,
...more
The constellation Cetus represents the Sea Monster. It is one of the largest constellations known. Even the ancient people of Mesopotamia recognized this large constellation. They believed the figure was
...more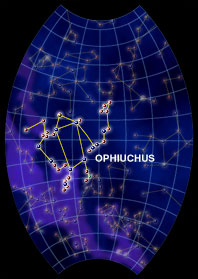
The constellation Ophiuchus represents the Serpent Bearer. This large constellation can be seen in the night sky from June through October. Although most of the stars are dim, Ophiuchus' teapot shape
...more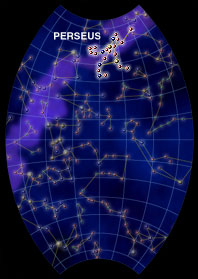
Perseus, the Hero, can be found in the sky during the winter in the Northern Hemisphere. With a little imagination, you can see the image of a man in the stars. He has a sort of triangular body, with
...more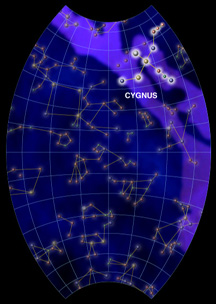
Cygnus, the Swan, is also known as the Northern Cross because of its distinctive shape. The tail of the swan is marked by the bright star Deneb, Arabic for "tail". Three fainter stars cross the line between
...more


 Questions and answers about the Milky Way
Questions and answers about the Milky Way
 A Matter of Scale - interactive showing the sizes of things, from very tiny to huge - from NSF
A Matter of Scale - interactive showing the sizes of things, from very tiny to huge - from NSF














