Click on image for full size
Copyright Roberta M. Johnson.
Atmospheric Science Literacy - Essential Principle 4
Earth's atmosphere changes over time and space, giving rise to weather and climate.
Fundamental Concept 4.1
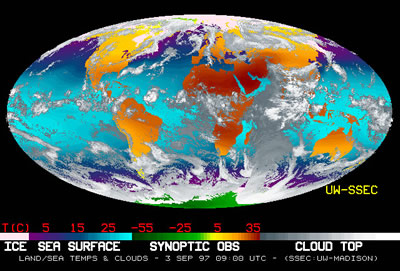
Weather is the state of Earth's atmosphere at a particular place and time. The climate of a particular place encompasses the long term range of weather conditions at that place. Earth's global climate is determined by the energy received from the Sun and is regulated by atmospheric composition and by atmospheric and oceanic circulation.
Fundamental Concept 4.2
Weather changes over time periods ranging from seconds to weeks. Climate changes over intervals ranging from years to millennia. Earth's history has been marked by gradual variations in global climate caused by long-term cyclic variations in Earth's orbit and axial tilt, and modulated by changes over geologic time in the sizes and distribution of the continents. These gradual variations have been punctuated by relatively abrupt climatic shifts caused by volcanic eruptions and sudden redistributions of mass and energy in the Earth System.
Fundamental Concept 4.3
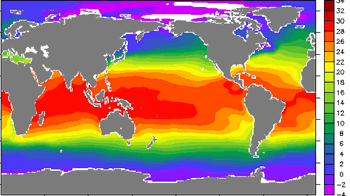
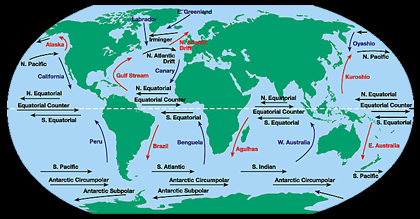
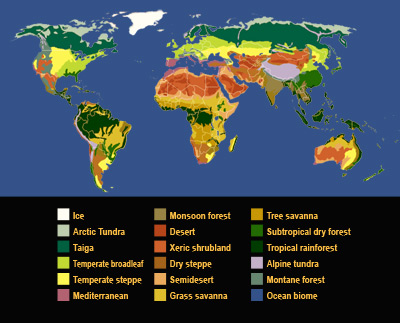
Both weather and climate vary by region based on latitude, altitude, land use, proximity to physical features such as the ocean and mountains, and ocean currents.
Fundamental Concept 4.4
Weather phenomena are important to human society. As evidenced in art, literature, and human culture over time, some atmospheric phenomena are beautiful, inspiring the human spirit. Severe weather, such as thunderstorms, tornadoes, and hurricanes, can bring rapid, dramatic changes to ecosystems and to individuals, property, and infrastructure.