An erupting, massive star in the Milky Way. NASA's Hubble Space Telescope has identified one of the most massive stars known, emitting as much as 10 million times the power of our Sun and with a radius larger than the distance between the Sun and the Earth.
Click on image for full size
Image courtesy of NASA, Space Telescope Institute
Fusion Inside the Stars
Fusion in the core of the stars is achieved when the density and
temperature arising
from the gravitational pressure are high enough.
There are different fusion cycles that occur in different phases of the
life of a star .
The first stage is the fusion of Hydrogen
into Helium. This is the stage that our Sun is in.
In stars with a very high temperature (greater than 16 million degrees
Kelvin)
another set of fusion reactions, the so called Carbon-Nitrogen-Oxygen
(CNO) cycle can take place.
Here the Carbon atom is a catalyst for the
reaction: it participates but it is not "burned".
At still higher temperatures,
Helium burning
produces Carbon. Finally, at even higher temperatures
the heavier elements up to Iron are formed by fusion of
Carbon, Oxygen and Silicon.
To create elements heavier than Iron,
neutron capture
must occur. This can happen in a
Supernova, when
a very massive star explodes at the end of its life
cycle.
As a result of the fusion reactions occurring in the Sun and stars,
neutrinos are emitted through the process of
beta decayand reach Earth. By
detecting these neutrinos, scientists learn about
fusion inside the stars.
You might also be interested in:
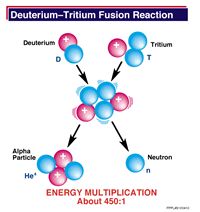
Nuclear fusion is a process where two or more nuclei combine to form an element with a higher atomic number (more protons in the nucleus). Fusion is the reverse process of nuclear fission. Fusion of light
...more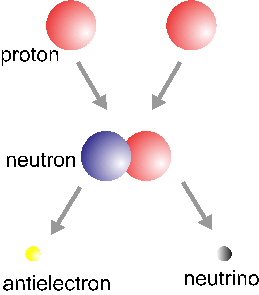
The basic Hydrogen fusion cycle involves four Hydrogen nuclei (protons) and two electrons and yields a Helium nucleus, two neutrinos and six photons. This process occurs in three steps: the first one is
...more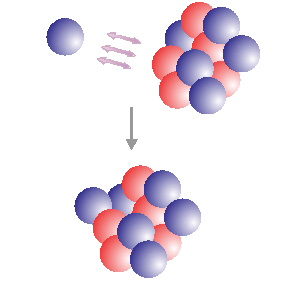
Neutron capture can occur when a neutron approaches a nucleus close enough for nuclear forces to be effective. The neutron is captured and forms a heavier isotope of the capturing element. When the new
...more
A Supernova is a very massive star that explodes at the end of its life cycle. The supernova is the furnace where the heavy elements (heavier than iron) are formed by neutron capture.
...more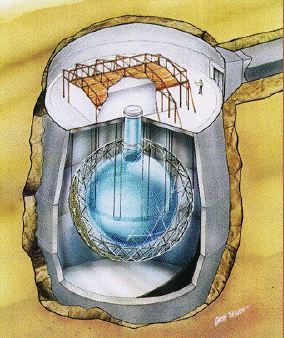
Neutrino interactions with matter are extremely rare, making detection difficult. Neutrino detectors are typically large tanks filled with a fluid that reacts to the passage of neutrinos. To take advantage
...more
The Sun, as well as other stars, releases energy in the form of radiation and particles. The processes that produce this energy are taking place in the interior of the Sun, where direct observations are
...more
Fusion in the core of the stars is achieved when the density and temperature arising from the gravitational pressure are high enough. There are different fusion cycles that occur in different phases of
...more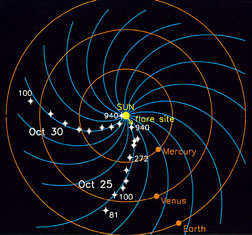
IMF stands for Interplanetary Magnetic Field. It is another name for the Sun's magnetic field. The Sun's magnetic field is enormous and is carried by the solar wind. The solar wind and magnetic field are
...more














