Image courtesy the Auroral Observatory of the University of Tromso, Norway.
Instruments & Techniques for Space Weather Measurements
Even though the Sun is very far away, it has a big effect on Earth. It gives us warmth and light. Storms on the Sun can also bring about what scientists call space weather on Earth or near Earth (just outside our atmosphere).
How do scientists measure space weather? Lots of different ways!
Space weather starts at the Sun, so scientists watch the Sun with special telescopes. Some of the telescopes are on Earth, and some are out in space.
Scientists use other special instruments to look at the different layers of the Sun or to find out what makes up the Sun.
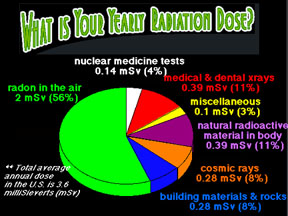
The Sun gives off light, but it also shoots out radiation. When radiation from the Sun hits Earth's atmosphere, the radiation can make the atmosphere "glow". Maybe you've seen this glow (also called Northern and Southern Lights)? Scientists measure the types and energy levels of the radiation that makes it to Earth from the Sun.
Scientists can tell a lot about the Sun by looking at how the Earth's atmosphere is reacting to particles that have arrived from the Sun. One layer of the atmosphere called the ionosphere is especially helpful for this. Scientists can look at how excited this layer is to see what might have come from the Sun to cause the excitement. Particles which are excited behave differently than ones that are more restful... sound like any students you know?
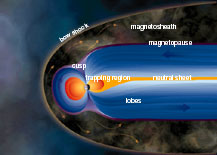
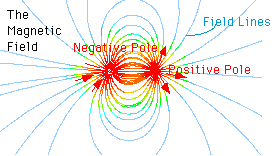
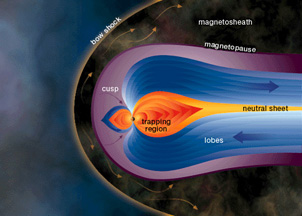
Magnetic fields are an important part of space weather. As space weather changes, magnetic fields change. Scientists use instruments called magnetometers to measure these changes. There are magnetometers at many places on Earth. There are also magnetometers on satellites in space.