This is an X-ray image of the Sun taken with the Soft X-Ray Telescope (SXT) on the orbiting Yohkoh satellite. This is an example of the deep, red images of the Sun you might've seen. This particular image was taken on November 23, 1999.
Click on image for full size
ISAS/Yohkoh team/Lockheed Palo Alto Research Laboratory
Yohkoh Mission
Have you ever wondered how scientists know so much about the Sun? Have you ever seen a deep, red picture of the Sun and wanted to know where it came from? Well, your questions may be answered! For most of this decade, the Yohkoh satellite has supplied us with tons of information about our closest star.
The Yohkoh Observatory was launched on August 31, 1991, from the island of Kyushu in Japan. Ever since, the satellite has sent back numerous X-ray and gamma ray images of the Sun. It uses four special instruments, two of which use spectroscopy. The other two use X-rays. Together, they send back spectacular images in light we can't normally see.
The main goal of the project was to increase our understanding of solar flares, which are sudden bursts of energy released by the Sun. Specifically, scientists want to know why X-rays and gamma rays are released during this type of event. However, the observatory also aids in the study of coronal mass ejections and other types of solar activity.
The Yohkoh satellite is controlled from the Institute for Space and Astronautical Sciences in Japan. On December 14, 2001, Yohkoh experienced a power shutdown to the scientific instruments. This power shutdown was triggered by an annular eclipse of the Sun that occurred over parts of the Pacific Ocean that same day. Efforts are being made to recover the spacecraft. Overall, the Yohkoh spacecraft has been highly successful and has provided real-time monitoring of solar activity for the sake of space weather studies.
You might also be interested in:

The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) was one of the most important exploration tools of the past two decades, and will continue to serve as a great resource well into the new millennium. The HST is credited
...more
Driven by a recent surge in space research, the Apollo program hoped to add to the accomplishments of the Lunar Orbiter and Surveyor missions of the late 1960's. Apollo 11 was the first mission to succeed
...more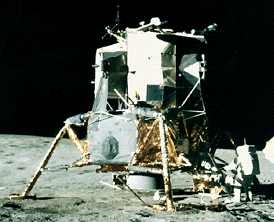
Apollo 12 survived a lightning strike during its launch on Nov. 14, 1969, and arrived at the Moon three days later. Astronauts Charles Conrad and Alan Bean descended to the surface, while Richard Gordon
...more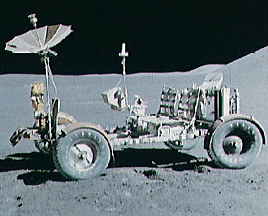
Apollo 15 marked the start of a new series of missions from the Apollo space program, each capable of exploring more lunar terrain than ever before. Launched on July 26, 1971, Apollo 15 reached the Moon
...more
NASA chose Deep Impact to be part of a special series called the Discovery Program on July 7, 1999. In May 2001, Deep Impact was given the "go" from NASA to start with mission development. Deep Impact
...more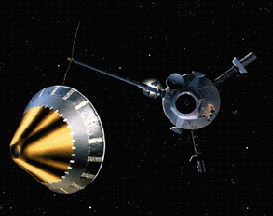
The Galileo spacecraft was launched on October 19, 1989. Galileo had two parts: an orbiter and a descent probe that parachuted into Jupiter's atmosphere. Galileo's primary mission was to explore the Jovian
...more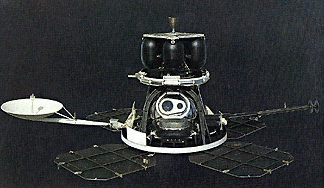
During 1966 through 1967, five identical Lunar Orbiter spacecrafts were launched, with the purpose of mapping the Moon's surface and finding smooth, level terrain, in preparation for the Apollo and Surveyor
...more















