An artist's concept of the CoRoT satellite in orbit.
Click on image for full size
CNES / D. Ducros
Related links:
CoRoT website
CoRoT - Searching for distant worlds
In December 2006, the European Space Agency launched a satellite that will
study convection and rotation in
pulsating stars. The mission will also
look for planets that pass in front of, or transit, these distant stars.
The lead scientists from France named the satellite CoRoT, which stands
for Convection, Rotation, and planetary Transits.
CoRoT will make very accurate measurements of the amount of light coming
from many stars over time. Some of these stars will have planets around
them. Some of those planets will pass directly in front of the star and
cause a brief drop in the amount of light CoRoT records. If these drops
happen regularly from the same star, if the color of the light does not
change, and if the shape of the drop is right -- it could be a planet.
Even planets as small as the Earth around other stars might be found with
CoRoT. This is about 10 times smaller than the smallest planets that have
been found from telescopes on the ground. If it finds a planet like the
Earth, then we can begin looking for signs of liquid water, green plants,
and maybe even intelligent life!
You might also be interested in:

Remember me? Last month I was observing targets of the Kepler space mission at Teide Observatory on Tenerife. Now I am in Chile to observe targets of the CoRoT space mission. CoRoT is a satellite devoted
...more
The Hubble Space Telescope (HST) was one of the most important exploration tools of the past two decades, and will continue to serve as a great resource well into the new millennium. The HST is credited
...more
Driven by a recent surge in space research, the Apollo program hoped to add to the accomplishments of the Lunar Orbiter and Surveyor missions of the late 1960's. Apollo 11 was the first mission to succeed
...more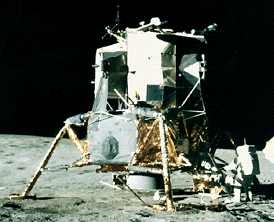
Apollo 12 survived a lightning strike during its launch on Nov. 14, 1969, and arrived at the Moon three days later. Astronauts Charles Conrad and Alan Bean descended to the surface, while Richard Gordon
...more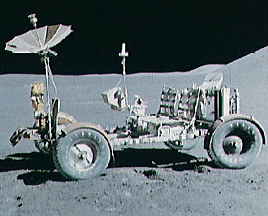
Apollo 15 marked the start of a new series of missions from the Apollo space program, each capable of exploring more lunar terrain than ever before. Launched on July 26, 1971, Apollo 15 reached the Moon
...more
NASA chose Deep Impact to be part of a special series called the Discovery Program on July 7, 1999. In May 2001, Deep Impact was given the "go" from NASA to start with mission development. Deep Impact
...more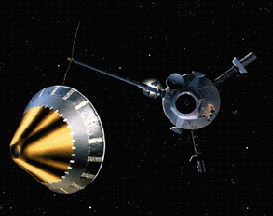
The Galileo spacecraft was launched on October 19, 1989. Galileo had two parts: an orbiter and a descent probe that parachuted into Jupiter's atmosphere. Galileo's primary mission was to explore the Jovian
...more















