Haumea (dwarf planet)
This page lists data and statistics about the dwarf planet Haumea.
| Size:* | 1,960 x 1,518 x 996 km (1,218 x 943 x 619 miles) [0.11 x Earth's] |
Orbital Semimajor Axis: (average distance from Sun) |
43.335 AU (Earth = 1 AU) |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mass: | 4.2 x 1021 kilograms (0.0007 x Earth's) |
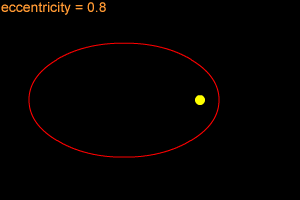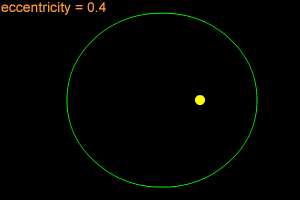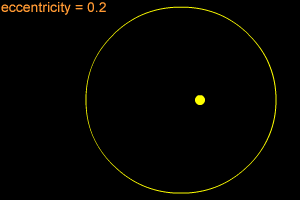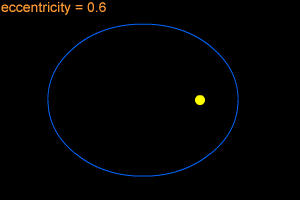
Orbital Eccentricity: | 0.18874 | ||
| Density: | 2,600-3,300 kg/m3 (0.47-0.60 x Earth's) |
Maximum Distance from Sun: | 51.526 AU ( 7.708 billion km or 4.790 billion miles ) |
||
| Surface Gravity: | 0.44 m/s2 (0.045 x Earth's) |
Minimum Distance from Sun: | 35.164 AU ( 5.260 billion km or 3.269 billion miles ) |
||
| Surface Temperature: | 32 K ( -241° C or -402° F ) |
Minimum Distance from Earth: | 34.147 AU ( 5.108 billion km or 3.174 billion miles ) |
||
| Tilt of Axis: | unknown | Orbital Inclination: (tilt of orbit plane) |
28.19° | ||
| Rotation Period about Axis: (length of Haumea's day) |
3 hrs 55 min | Revolution Period about the Sun: (length of Haumea's year) |
285.4 years | ||
|
Satellites: | known | |||
* Haumea is not spherical in shape; it is elongated into an ellipsoid (3D ellipse) shape because it spins so rapidly. Its size is, therefore, not given as a single diameter (as is the case with most planets), but in terms of its length along its three main axes. Its size, as compared to Earth, is based on comparing the size Haumea would have if it were "squashed" into a spherical shape.
 Comparative Planetary Statistics -- in table form
Comparative Planetary Statistics -- in table form
 Comparative Orbital Statistics -- in table form
Comparative Orbital Statistics -- in table form