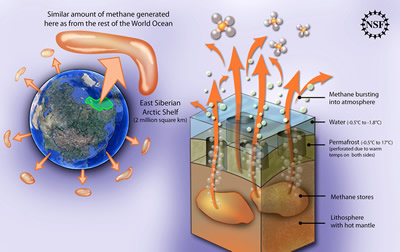
The permafrost of the East Siberian Arctic Shelf (an area of about 2 million kilometers squared) is more porous than previously thought. The ocean on top of it and the heat from the mantle below it warm it and make it perforated like Swiss cheese. This allows methane gas stored under it under pressure to burst into the atmosphere. The amount leaking from this locale is comparable to all the methane from the rest of the world's oceans put together. Methane is a greenhouse gas more than 30 times more potent than carbon dioxide.
Click on image for full size
Image Courtesy of Zina Deretsky, National Science Foundation
Methane Is Being Released Much Faster Than Previously Thought from the Arctic Ocean
Natalia Shakhova and Igor Semiletov, scientists from the University of Alaska Fairbanks, have led a research team to study a section of the sea floor of the Arctic Ocean in an area called the East Siberian Arctic Shelf. The results of their research show that the permafrost under this ice shelf is starting to leak large amounts of methane into the atmosphere.
Methane is a greenhouse gas that can be released from permafrost when the permafrost thaws on land or on the sea floor. The releases from the sea floor can be larger and happen more quickly than the releases on land.
The East Siberian Arctic Shelf is shallow, which means it has been both under water and above water at different times during Earth's history. During the Earth's coldest periods, it is a frozen arctic coastal plain, and does not release methane. As the Earth warms and sea level rises, the shelf is covered with seawater, which is 12-15 degrees warmer than the average air temperature.
In the deep water of the ocean, methane gas oxidizes into carbon dioxide before it reaches the surface. In the shallow water of the East Siberian Arctic Shelf, methane doesn't have enough time to oxidize, which means more of it escapes into the atmosphere. This can cause the climate to warm.
"The Arctic is a difficult place to get to and to work in, but it is important that we do so in order to understand its role in global climate and its response and contribution to ongoing environmental change," said Henrietta Edmonds of the National Science Foundation.
You might also be interested in:

When the ground under your feet is frozen, interesting things can happen. The land may be covered with circles, polygons, or stripes, called patterned ground, which form as the land freezes. Trees may
...more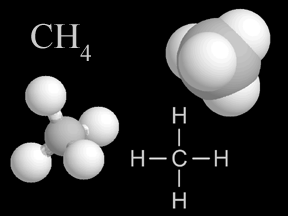
Methane is a kind of gas. There is a small amount of methane in the air you breathe. A methane molecule has carbon and hydrogen atoms in it. Methane is a greenhouse gas. That means it helps make Earth
...more
Even though only a tiny amount of the gases in Earth’s atmosphere are greenhouse gases, they have a huge effect on climate. There are several different types of greenhouse gases. The major ones are carbon
...more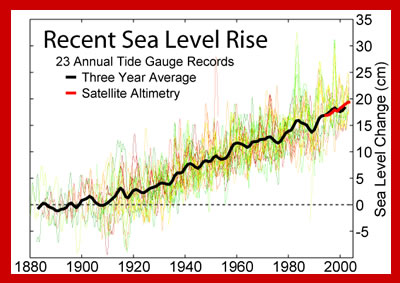
The coast of Bangladesh is home to millions of people, however rising sea level caused by global warming is expected to change that. This South Asian country is one of many low coastal areas worldwide
...more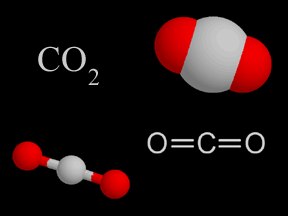
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a kind of gas. There isn't that much carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere, but it is still very important. Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas. That means it helps trap heat coming
...more
Scientists have learned that Mount Hood, Oregon's tallest mountain, has erupted in the past due to the mixing of two different types of magma. "The data will help give us a better road map to what a future
...more
The Earth's mantle is a rocky, solid shell that is between the Earth's crust and the outer core, and makes up about 84 percent of the Earth's volume. The mantle is made up of many distinct portions or
...more