Click on image for full size
NASA.
Solar Wind
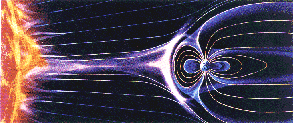
The Sun produces a constant stream of particles which billow out into space. In fact, 1 million tons of particles come from the Sun every second! This stream of particles is called the solar wind.
The solar wind plasma is very thin. Near the Earth, the plasma is only about 6 particles per cubic centimeter, compared to 2.5 10^19 molecules/cm3 in the Earth's sea-level atmosphere.Nevertheless, it is responsible for such unusual phenomena as:
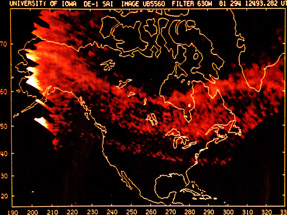
- aurorae
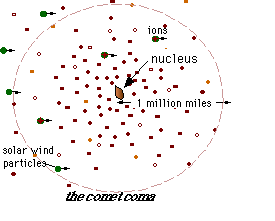
- ionizing comet coma
- fueling magnetospheric storms
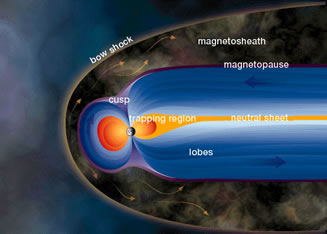
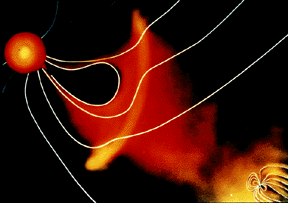
- forming a planet's magnetosphere and then driving circulation within the magnetosphere
The solar wind consists mostly of protons and electrons, but it also consists of ions of almost every element in the periodic table. It is considered to be the continual expansion of the Sun's atmosphere.It is a remmnant of the T-Tauri phase of stellar evolution when the newly ignited Sun blew massive quantites of its residual mass into space.
The solar wind emanates from the Sun in all directions, but seems to emmanate most readily from the Sun's coronal holes. Exactly what causes the solar wind to be accelerated, or "blown" into space is not well understood. Such phenomenon are being investigated by the SWICS and SWOOPS instruments of the Ulysses mission.
The particles of the solar wind, and the Sun's magnetic field (IMF) are stuck together, therefore the solar wind carries the IMF (interplanetary magnetic field) with it into space. Once blown into space, the particles travel at supersonic speeds of 200-800 km/sec and do not slow down until they reach the termination shock within the heliosphere, where the solar wind slows from supersonic to subsonic speeds. The Heliosphere is the entire region of space influenced by the Sun.