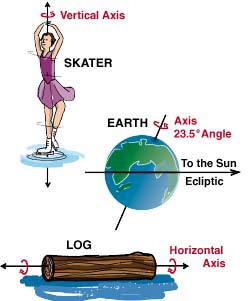
This image shows different objects that rotate. Rotational period is the time it takes for that object to rotate just once.
Rotational Period
Rotational period is the term describing the length of time necessary for a space object to make one complete rotation. This time varies from planet to planet, and on Earth it is 1 day.
This length of time is not constant, and in fact the Earth’s rotational period is slowing (by 0.002 seconds every hundred years). This is because of the Moon’s influence on our rotation. Sometimes collisions are also thought to slow rotational periods, and this is how scientists explain Venus’ rotation. Venus has a retrograde (backwards) rotation, and it is very slow. In fact, it is so slow that it revolves around the Sun faster (by about 17 Earth days) than it spins around its own axis. This means that a Venus day is longer than a Venus year!
You might also be interested in:
AU stands for Astronomical Units. Distances in space are too large to measure in Earth standards like miles or kilometers. For distances too large to measue in AU, we use light years. A light year is the
...more
The solar wind is formed as the Sun's topmost layer blows off into space carrying with it magnetic fields still attached to the Sun. Gusts and disturbances form in the solar wind associated with violent
...more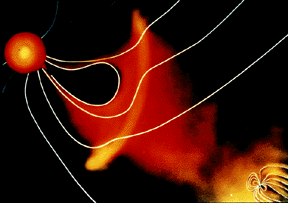
For a planet to be affected by a blob of material being ejected by the sun, the planet must be in the path of the blob, as shown in this picture. The Earth and its magnetosphere are shown in the bottom
...more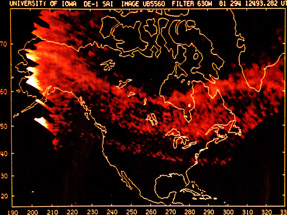
The aurora we are most familiar with is the polar aurora. This is what people are referring to when they speak of the northern or southern lights. But there are other less-known auroral activity, such
...more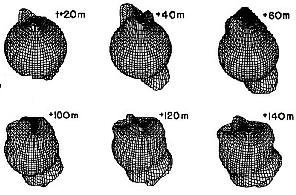
This figure shows the effect of the aurora on the atmosphere. When FAC's enter the atmosphere and create the aurora, they warm the atmosphere impulsively. This impulse travels throughout the atmosphere
...more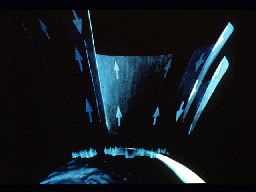
This picture illustrates the streaming of particles into and out of the auroral zone, as Field-aligned currents (FAC's) short-circuit through the ionosphere. Some of the particles entering the auroral
...more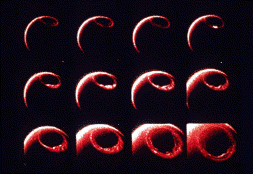
This figure shows a series of images of the auroral oval as it expands over the course of about an hour in response to a geomagnetic storm. This is an animation of the expanding auroral oval.
...more