Glossary : Greenhouse Gas
A gaseous component of the
atmosphere contributing to the
greenhouse effect. Greenhouse gases are transparent to certain
wavelengths of the sun's radiant energy, allowing them to penetrate deep
into the atmosphere or all the way into the Earth's surface. Greenhouse
gases and clouds prevent some of the infrared radiation from escaping,
trapping the heat near the Earth's surface where it warms the lower
atmosphere. Alteration of this natural barrier of atmospheric gases can
raise or lower the mean global temperature of the Earth.
Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide,
chloroflurocarbons, and water vapor. Carbon dioxide, methane,
and nitrous oxide have significant natural and human sources while only
industries produce chloroflurocarbons. Water vapor has the largest
greenhouse effect, but its concentration in the troposphere is
determined within the climate system. Water vapor will increase in
response to global warming, which in turn may further enhance global warming.
Courtesy of NASA
You might also be interested in:
AU stands for Astronomical Units. It is a useful way to measure the distances in interplanetary space. It is the distance between the Earth and the Sun, which is about 93 million miles. For reference,
...more
The solar wind is formed as the Sun's top layer blows off into space, carrying magnetic fields still attached to the Sun. Gusts form in the solar wind associated with violent events on the Sun. Particles
...more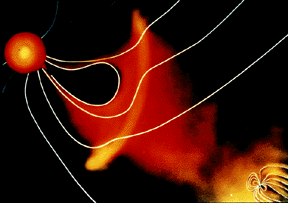
For a planet to be affected by a blob of material being ejected by the sun, the planet must be in the path of the blob, as shown in this picture. The Earth and its magnetosphere are shown in the bottom
...more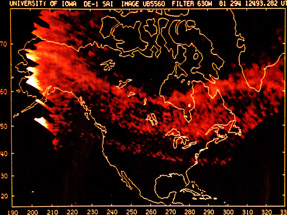
The aurora we are most familiar with is the polar aurora. This is what people are talking about when they say the northern or southern lights. But there are other less-known aurora, such as SAR arcs.
...more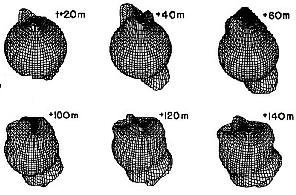
This figure shows the effect of the aurora on the atmosphere. When FAC's enter the atmosphere and create the aurora, they heat the atmosphere suddenly and abruptly. This creates an impulse which travels
...more
This picture shows the flowing of particles into and out of the auroral zone, as Field-Aligned currents (FAC's) take at short-cut through the atmosphere. Some of the particles entering the auroral zone
...more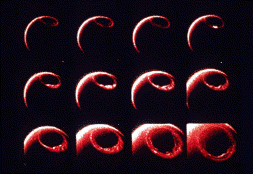
This figure shows a series of images of the auroral oval as it expands over the course of about an hour in response to a geomagnetic storm. This is an animation of the auroral oval expanding.
...more














