Click on image for full size
Image Courtesy of Dennis Ward/UCAR
Related links:
Latitude and Longitude
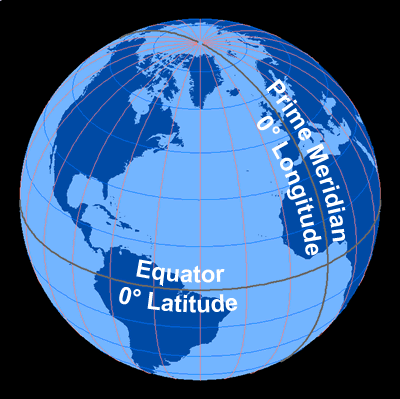
The most common way to locate points on the surface of the Earth is by standard, geographic coordinates called latitude and longitude. These coordinates are measured in degrees and represent angular distances calculated from the center of the Earth. On maps and globes, these are drawn as imaginary lines of latitude and longitude and help us determine locations.
Latitude describes the distance from the Earth's equator and is measured in angular degrees, with 0 degrees being the equator. The North Pole is +90 degrees and the South Pole is -90 degrees. Latitude is also described as being either “North” or “South,” depending on the position in relationship to the equator. Positive latitude values are indicated by “North” and negative values are indicated by “South." The equator divides the Earth into Northern and Southern Hemispheres. A line connecting all the points with the same latitude value is called a line of latitude.
Longitude is the angular measurement either east or west from the Prime Meridian, a line of longitude which runs between the poles and through Greenwich, England. Lines of longitude run perpendicular to lines of latitude. Longitude increases as you leave the Prime Meridian (0 degrees) going east (0 to 180 degrees) and decreases as you head west (0 to -180 degrees), until they meet at 180 degrees. Positive longitude values are also indicated by “East” and negative values are indicated by “West." The Prime Meridian divides the Earth into Eastern and Western Hemispheres. Why a line through Greenwich, England? It could be anywhere, but in the mid-1800s the Royal Observatory in Greenwich, England was well known for keeping time, and because the time is the same all along that line of longitude, it was decided that the Prime Meridian would go through Greenwich.
Here's an example of the latitude and longitude of a specific location. New York, NY, USA has a latitude of 40.75793 degrees (north) and a longitude of -73.98551 (west). This means New York, NY is approximately 41 degrees north of the equator and approximately 74 degrees west of the Prime Meridian.
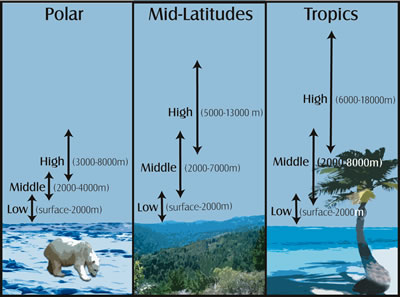
A region's latitude has a great effect on its climate because latitude determines the amount of solar energy a region receives. Low latitude locations, on or near the equator, are called the tropics. It's warm there because roughly the same amount of sunlight is received year-round. High latitude locations, at or near the poles, have a cold, polar climate. The closer you are to one of Earth's poles, the less sunlight there is during winter days. Mid-latitude climates in the areas between the tropics and polar regions are often characterized by having several distinct seasons throughout the year because the amount of sunlight changes from summer to winter.
We use longitude to determine time zones on Earth. The Earth is a sphere that has 360 degrees, and it makes a complete rotation every day. Every 15 degrees of longitude on Earth represents a different time zone.