Courtesy of NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center Scientific Visualization Studio
Where Do Earthquakes Happen?
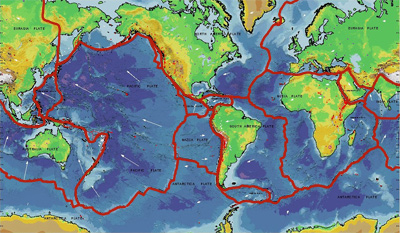
The animation at the left shows where in the world earthquakes, represented as yellow dots, happened between 1960 and 1995. Do you see a pattern?
Earthquakes do not happen at random locations. They are not equally spaced. Some areas have many earthquakes while other areas have few.
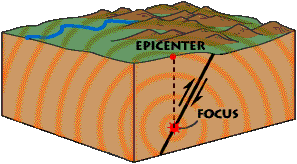
Earthquakes happen when rock below the Earth's surface moves abruptly. Usually, the rock is moving along large cracks in Earth's crust called faults. Most earthquakes happen at or near the boundaries between Earth's tectonic plates because that's where there is usually a large concentration of faults. Some faults crack through the Earth because of the stress and strain of nearby moving plates. Other, large faults are the boundary between plates, such as the San Andreas Fault on the North American west coast.
Since earthquakes happen along faults and most active faults are near plate boundaries, those clusters of yellow dots in the animation tell us where the boundaries between Earth's tectonic plates are located.
While it is not as common, there are also some active faults in the middle of plates. And just like other faults, movement along those faults can cause earthquakes as well. For example, within the North American tectonic plate numerous earthquakes occurred in the Mississippi River Valley between December 1811 and March 1812, some very strong. These earthquakes happened because of movement along the New Madrid Fault near the town of New Madrid, Missouri, U.S. Many of these earthquakes still rank among the largest felt in the United States since the European settlement.