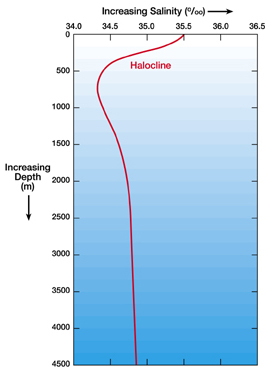
This image shows a generalized salinity-depth profile for the South Atlantic Ocean.
Click on image for full size
Windows Original
Standard Salinity Profile
This is a
salinity versus depth profile for ocean water. This salinity versus depth profile is typical of the South Atlantic ocean. Salinity versus depth profiles at other locations in
the ocean could look quite different.
In this profile, salinity at the surface is high and then salinity decreases until a depth of about 1,000 meters. Salinity then increases again slightly with increasing depth.
The halocline is a layer of water where the salinity changes rapidly with depth.
You might also be interested in:
About 70% of the Earth is covered with water. Over 97% of that water is found in the oceans. Everyone who has taken in a mouthful of ocean water while swimming knows that the ocean is really salty! Dissolved
...more
The majority of the world's population does not live in the Arctic. But even if you don't live in the Arctic, it is very important to understand how the Arctic Ocean works because it has an impact on surrounding
...more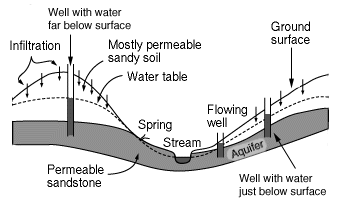
An aquifer is the name for a layer of rock which is capable of holding a large amount of water. Some layers are better at holding water than others, for example a layer of sandstone can hold a good deal
...more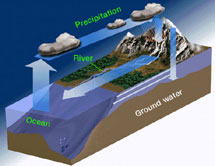
Carbonate is a name for rocks and minerals which contain a molecule made of both carbon and oxygen known as CO32-. (CO32- is also known as the molecule carbonate). Limestone is an example of a calcium
...more
One process which transfers water from the ground back to the atmosphere is evaporation. Evaporation is when water passes from a liquid phase to a gas phase. Rates of evaporation of water depend on things
...more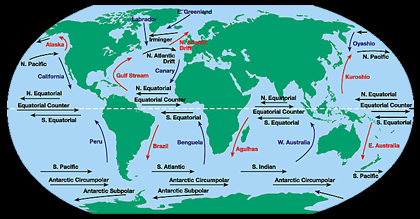
The water at the ocean surface is moved primarily by winds that blow in certain patterns because of the Earth’s spin and the Coriolis Effect. Winds are able to move the top 400 meters of the ocean creating
...more
Rivers are very important to Earth because they are major forces that shape the landscape. Also, they provide transportation and water for drinking, washing and farming. Rivers can flow on land or underground
...more