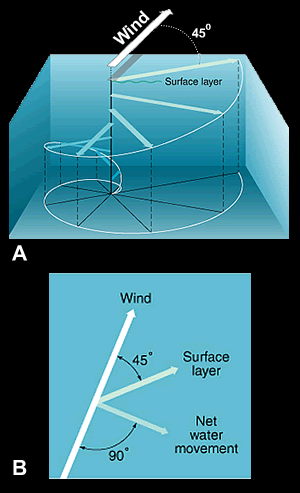
An Ekman spiral (A) is a rotating column of water that forms when water moves at an angle to the wind direction due to the Coriolis Effect. The net effect of the rotating water (B) is movement at right angle to the wind direction. The example shown above is for the Northern Hemisphere. The water turns to the left instead of right in the Southern Hemisphere.
Click on image for full size
NOAA
How the Ocean Surface Moves
As Arctic explorer Fridtjof Nansen tried to get to the North Pole in 1893, he noticed that the sea ice in the Arctic Ocean was not moving in the same direction as the wind. It was always moving to the right of the wind direction. Nansen didn’t know why this was happening. Today we do. It is called Ekman transport.
As wind blows across the ocean, it moves water at the surface. Because the Earth rotates, water moves to the right of the wind in the Northern Hemisphere and to the left of the wind in the Southern Hemisphere.
The water deeper down changes direction. The water underneath the surface turns a bit more, and the water below that turns even more. This makes a spiral of moving water 100 to 150 meters (330 to 500 ft) deep. The average direction of all this turning water is about a right angle (90°) from the wind direction. This average is Ekman transport.
Ekman transport is named for Swedish scientist V. Walfrid Ekman who first described the spiral of water in 1905. To help him make a model of these movements, Ekman used the observations that Nansen made while he was in the Arctic.
You might also be interested in:

In the Arctic, you will find the Arctic Ocean surrounded by the continents of Europe, Asia, and North America. You will find the geographic North Pole and the magnetic North Pole there; both are in the
...more
Sea ice is frozen seawater. It floats on the oceans that are in Earth's polar regions. The salt in the seawater does not freeze. Very salty water gets trapped in the sea ice when it forms. The pockets
...more
Wind is moving air. Warm air rises, and cool air comes in to take its place. This movement creates the winds around the globe. Winds move at different speeds and have different names based on their speed.
...more
There are places in the ocean where water from the deep sea travels up to the surface. These are called areas of upwelling. The deep waters can have a large influence on marine life and the climate too.
...more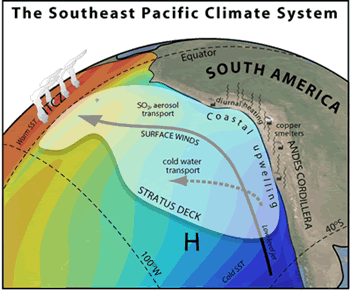
There are a lot of clouds over the Southeast Pacific Ocean off the coasts of Peru and Chile in South America. In fact, this area has the largest amount of stratus and stratocumulus clouds in the world!
...more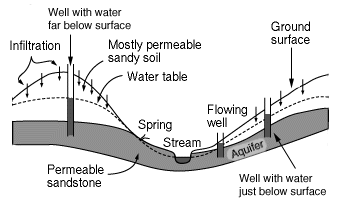
An aquifer is the name for a layer of rock which is capable of holding a large amount of water. Some layers are better at holding water than others, for example a layer of sandstone can hold a good deal
...more
Limestone is an example of a carbonate. Other examples of carbonates include calcite, dolomite, and marble. Limestone dissolves easily in rainwater, especially rainwater which is loaded with carbonic acid.
...more