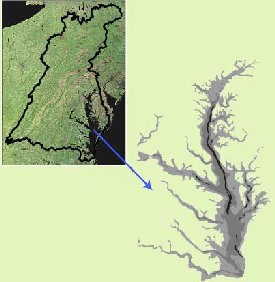
To the left is a satellite image of the Chesapeake Bay area. The black line superimposed on the satellite image marks the boundary of the Chesapeake Bay watershed. The grey image on the right shows the details of Chesapeake Bay.
Click on image for full size
Courtesy of USGS (United States Geological Survey
Chesapeake Bay
Chesapeake Bay is the largest of 130 estuaries in the United States.
Rivers, streams and
ground water drain into Chesapeake Bay where this fresh water mixes with the salt water from the Atlantic
Ocean. This mixing of fresh water and
salt water is what makes this an
estuary.
The area surrounding the Bay is called the Chesapeake Bay watershed. The watershed is all the areas that have water that ultimately drains into the Bay. The Chesapeake Bay watershed is big! It includes parts of six states, New York, Pennsylvania, Delaware, Maryland, Virginia, and West Virginia, and all of the District of Columbia. The black line on the satellite image to the left outlines the Chesapeake Bay watershed.
Chesapeake Bay stretches from Havre De Grace, Maryland, to Norfolk, Virginia. It is a shallow bay, averaging only 21 feet deep. The Bay's widest point is 35 miles across near the mouth of the Potomac River.
Estuaries are special places where life thrives! Chesapeake Bay is no exception! The Bay watershed is home to more than 3,600 species of plants and animals. The Bay watershed is also home to 15.1 million people.
Humans have a huge effect on the other life in Chesapeake Bay. According to the Chesapeake Bay program, " each time a person uses electricity, drives a car or even drops a piece of trash, a chain of events that can affect the Bay occurs." Organizations like the Chesapeake Bay program are trying restore the Bay. They are helping people reduce pollution, restore plants that reduce erosion, and monitor the Bay's health. Many universities, companies and schools are helping to monitor the Bay's health by taking measurements of the water in the Bay. One such program is the HIGH TIDE program that involves area high schools that are making measurements of the water in the Bay in order to note changes in salinity, temperature and density.
You might also be interested in:

What types of instructional experiences help K-8 students learn science with understanding? What do science educators teachers, teacher leaders, science specialists, professional development staff, curriculum designers, school administrators need to know to create and support such experiences?
...more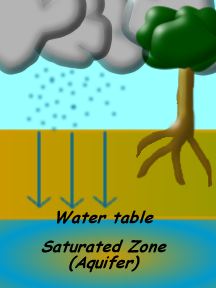
Most of the water we see each day is in ponds, rivers, oceans, streams, lakes, puddles, and other places on top of the ground. What we don’t often see is the water that soaks into the ground. Water that
...more
Earth's ocean covers more than 70% of our planet's surface. There are five major ocean basins. The Pacific Ocean is the largest. It’s so large that it covers a third of the Earth's surface. The Atlantic
...more
An estuary is a very special place where fresh water and salt water come together. Estuaries are found on the coast where fresh water like a river or a bay has access to the ocean. A good example of an
...more
Chesapeake Bay and its watershed support more than 3,600 species of plants, fish and animals. 2,700 species of plants alone live in the Chesapeake Bay area. These plants serve as the base for the foodchain
...more
With over 2 million species, Kingdom Animalia is the largest of the kingdoms in terms of its species diversity. But when you think of an "animal", what image comes to mind? While mammals, birds, reptiles,
...more
When we measure the salinity of water, we look at how much dissolved salt is in the water, or the concentration of salt in the water. Concentration is the amount (by weight) of salt in water and can be
...more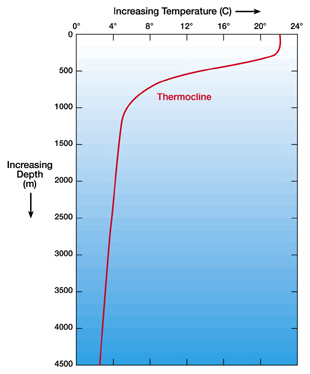
If you want to know about the temperature of the ocean, you have to learn about the parts of the the ocean first. The top part of the ocean is called the surface layer. Then there is a boundary layer called
...more