Greg Anderson, Bates College, Departamento de Biología.
Air Pollution Affects Plants, Animals, and Environments
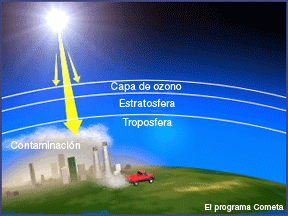
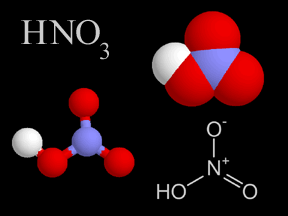
Acid rain harms living things
Did you know that air pollution can change the rain? And all living things need rain for water to drink, or to swim within. The rain changed by air pollution is called acid rain. Acid rain kills trees and harms animals. Acid rain can destroy the leaves of plants like in this picture. When acid rain soaks into the ground, it can make the soil unhealthy for many living things. Acid rain also changes the water in lakes and streams, harming fish and other aquatic life.
Ozone holes harm living things
Some air pollutants have damaged parts of the ozone layer high in the atmosphere. The ozone layer protects our planet from the Sun's harmful rays. The areas of thin ozone are called ozone holes. These strong rays from the Sun cause skin cancer and damage plants and wildlife.
Ozone near the ground harms living things
Pollution releases ozone near the ground. Ozone molecules near the ground hurt the lungs of animals and people and prevent plants from breathing by blocking the openings in leaves where they breathe. Without breathing, a plant is not able to grow.
Global warming harms living things
Our planet is currently warming quickly. The extra warmth is caused by greenhouse gases from air pollution. Greenhouse gases are released into the atmosphere when fuels are burned. Plants can make some of the greenhouse gases into oxygen in the air and carbon to grow their leaves, stems, and trunks larger. However, the amount of greenhouse gases released in air pollution is much more than plants can use.
Global warming is causing changes to the places where plants and animals live around the world. For example:
- Near the poles, ice and frozen ground are melting. This causes changes in the habitat and resources for plants and animals living there.
- Ocean warming, rising sea levels, runoff, and coral diseases are causing change in shallow marine environments such as coral reefs.
- Global warming is causing less rain to fall in the middle of continents. This makes these areas very dry and limits water resources for plants and animals.