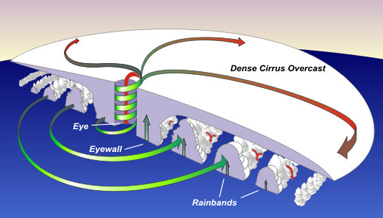
Click on image for full size
Courtesy of USGS
Hurricane Damage
Rain, wind, tornadoes, and storm surge related to hurricanes cause change to natural environments, damage to the human-built environment, and even loss of life.
When a hurricane is over the ocean and far from land, wind and large waves created by the storm are a hazard for boats at sea. But with modern forecasting and warning systems, boats can steer clear of a hurricane. Before forecasting and warnings became common, hurricanes were the cause of many shipwrecks including several in the Bermuda Triangle, an area known for disappearing ships. Unlike boats, oil and gas platforms over the water are unable to move out of harms way and can be damaged by the fierce wind and waves.
When a hurricane approaches land, tremendous damage can occur in the built environment. The amount of damage depends both on the intensity of the storm and what it hits. A combination of winds, storm surge, and rain cause great damage to buildings, power lines, roads, and automobiles. During hurricane Katrina in 2005 levees broke causing much of the city of New Orleans, LA to flood. The damage to the US Gulf coast caused by Hurricane Katrina was the most costly in US history.
Hurricanes cause many changes to the natural environment along a coast too. Sand is eroded from some coastal areas and deposited in others. The waves and storm surge are able to carry large rocks and even boulders. Many low-lying areas are flooded by storm surge. And strong winds and floods can thin or destroy forests.
After a hurricane hits a coastal area, it can travel inland. At this point, the storm has typically weakened, but it can still cause serious damage. Torrential rains from the storm can cause flooding and mudslides.
It is estimated that 10,000 people die each year worldwide due to hurricanes and tropical storms. The majority of human deaths are caused by flooding. Because they can be very dangerous, it is important to look for hurricane warnings and to evacuate if it is recommended in your area. If you live in a hurricane prone area, visit the Hurricane Preparedness web site at the US National Hurricane Center for tips on how to prepare for a hurricane.