This is a drawing of the transition from the atmosphere to the interior.
Click on image for full size
NASA
The Layers of Saturn's Interior
There is no surface to the giant planets, only a gradual change from the atmosphere, as shown in this drawing.
The gases which Saturn is mostly made of change to liquid inside Saturn, but the change is very slow. This means that the giant planets do not have real layers on the inside, as the earth-like planets do.
The liquid sections of Saturn are the biggest parts of the planet and go down very deep (the liquid is not made of water!). The first liquid layer inside Saturn, right under the atmosphere, is the liquid hydrogen layer. Under the liquid hydrogen layer is a liquid metallic hydrogen layer.
At the deepest part of Saturn is the core.
You might also be interested in:

The first liquid layer inside Saturn, right under the atmosphere, is a layer of liquid hydrogen!. The air becomes thicker and thicker, like a dense fog, with more and more liquid drops, until the hydrogen
...more
The Giant planets do not have the same kind of layers inside that the earth-like planets do. The history of the giant planets was so different that they formed with much more gas on the inside. Saturn
...more
There is no surface to the giant planets, only a gradual change from the atmosphere, as shown in this drawing. The gases which Saturn is mostly made of change to liquid inside Saturn, but the change is
...more
The most important motions in the atmosphere are winds. The major winds in Saturn's atmosphere are the zonal winds which are made of zones and belts. Zones and belts blow in opposite directions around
...more
The clouds on Saturn, like Jupiter, are divided into stripes called "belts and zones". In a belt, very powerful winds blow one way. In a zone, very powerful winds blow the other way. These kinds of winds
...more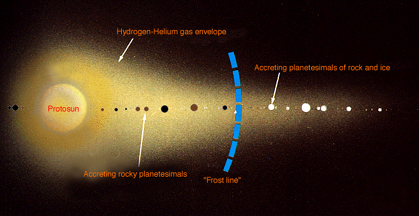
The position of the planets in the solar nebula affected how big they became and what they were made of. The blue line in the picture shows where it became so cold that ice began to form. Planets that
...more
As shown in this picture, while they were forming in the solar nebula, the core of the planets-to-be drew material to themselves from the cloud of gas and dust around them. The bigger planets-to-be were
...more














