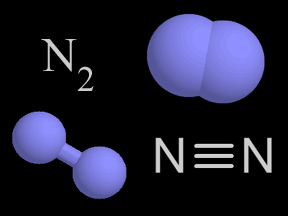Photodissociation of Molecular Nitrogen (N2)
|
This animation illustrates the process of photodissociation of nitrogen. When an extreme ultraviolet (EUV) photon strikes a nitrogen molecule, it photodissociates the molecule into two separate nitrogen atoms. The energy from the photon breaks the chemical bond that holds the molecule together. The result is two separate nitrogen atoms.
You will need to have the latest version of the Flash player to see this animation.
|
 Photodissociation of Molecular Oxygen
Photodissociation of Molecular Oxygen
 Photodissociation of Water
Photodissociation of Water
 Photodissociation of the Hydroxyl Radical
Photodissociation of the Hydroxyl Radical
You might also be interested in:

Sometimes when a photon hits a molecule, the energy from the photon causes the molecule to break apart. Scientists use the term "photodissociation" for such events. Photodissociation plays a very important
...more
Light is very strange. Sometimes it is best to think of light as a series of waves. At other times, it is useful to think of light as a swarm of particles. When we think of light as particles, we call
...more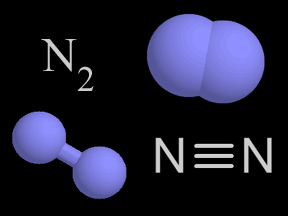
Nitrogen is a chemical element with an atomic number of 7 (it has seven protons in its nucleus). Molecular nitrogen (N2) is a very common chemical compound in which two nitrogen atoms are tightly bound
...more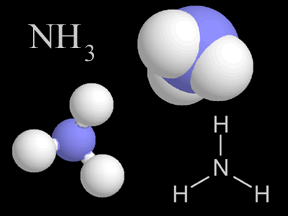
Most things around us are made of groups of atoms bonded together into packages called molecules. The atoms in a molecule are held together because they share or exchange electrons. Molecules are made
...more
The thermosphere is a layer of Earth's atmosphere. The thermosphere is directly above the mesosphere and below the exosphere. It extends from about 90 km (56 miles) to between 500 and 1,000 km (311 to
...more
Triton, by far the largest moon of Neptune, is slightly smaller than Earth's Moon. Triton has the coldest surface temperatures in our Solar System. Surprisingly, this frigid moon has an atmosphere, albeit
...more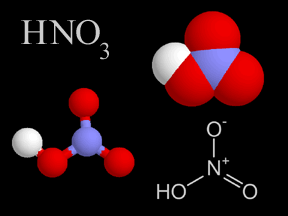
Nitric acid is a colorless, corrosive liquid and a toxic acid which can cause severe burns. Nitric acid consists of nitrogen, oxygen, and hydrogen atoms. Nitric acid, in its gas phase, is present in very
...more
 Photodissociation of Molecular Oxygen
Photodissociation of Molecular Oxygen
 Photodissociation of the Hydroxyl Radical
Photodissociation of the Hydroxyl Radical