Image courtesy George Varros.
Geminid Meteor Shower
The Geminid meteor shower happens every year in December. Meteor showers are times when you can see many meteors or "shooting stars" in one night. There are several meteor showers each year. Most meteor showers can be seen for several nights. Usually, there is one night when you can see the most meteors. That night is called the "peak" of the meteor shower. The peak of the Geminid shower is around December 14th.
During a meteor shower, it looks like all of the meteors shoot outward from one place in the sky. That point in the sky is called the "radiant" of the meteor shower. Each shower has a different radiant. The radiant for the Geminid shower is in the constellation Gemini. That is why this shower is called the "Geminids".
If you want to see Geminid meteors, go outside at night on December 14th or one of the nights just before or after that date. You can see more meteors if you can watch from someplace very dark, away from street lights. If you are lucky, you might see as many as 100 meteors in an hour!
Most of the Geminid meteoroids are very, very small - about the size of a grain of sand! However, they are moving very, very fast - around 35 km/s (about 78,000 mph)! When they hit Earth's atmosphere, they burn up and glow; the glowing trails they leave behind for a second or two are what we see as meteors.
Can you guess where meteors come from? Most meteoroids in meteor showers are actually dust from a comet! When a comet gets near the Sun and heats up, its ices melt and dust trapped in the ice escapes into space. The dust spreads out over the comet's orbit. When Earth crosses the comet's orbit, we run into the dust - and see a meteor shower!
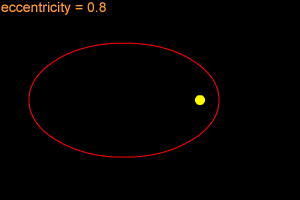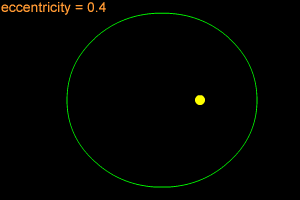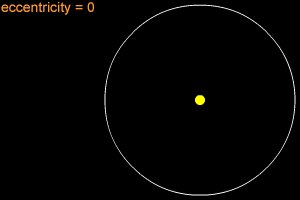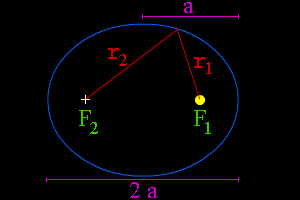
The Geminids are a strange meteor shower. People have known about most of the big meteor showers for many, many years. But not the Geminids! The first time anyone noticed the Geminids was in 1862. At that time, there were only about 15 meteors per hour in the Geminids. Astronomers started looking for the comet that the Geminids came from. They couldn't find one! Finally, in 1983 a satellite named IRAS (Infrared Astronomical Satellite) discovered an object in the right orbit to make the Geminids. The object is named 3200 Phaethon. The strange object looks more like an asteroid than a comet. Maybe 3200 Phaethon is an asteroid that crashed into another asteroid, making a cloud of dust and small rocks. Maybe that cloud is what makes the Geminid meteor shower. Or maybe 3200 Phaethon isn't an asteroid after all. Maybe it is an old, "dead" comet that has lost all of its ice. Scientists aren't quite sure which is true.