Where are we now? Climate "Today"
Before we move on to projections of future state of our planet's climate, let's take a few looks at the current state of Earth's climate.
These graphs show how carbon emissions, atmospheric concentrations of carbon dioxide, and global average temperatures have changed in recent times.



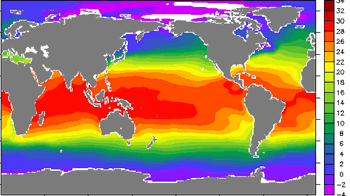
This image shows sea surface temperatures (SST) averaged over a whole year (in this case, 2001). Notice how temperatures range from freezing (0° C or 32° F) near the poles to around 30° C (about 86° F) in the tropics.
Credits: Image courtesy of Plumbago via Wikipedia, using data from the World Ocean Atlas 2001. |
Here is Earth's surface air temperature in recent times. This image shows average temperatures for the period from 1961 to 1990.
Credits: Image courtesy of Robert A. Rhohde and the Global Warming Art project. |
This map (above) shows recent changes in Earth's surface air temperatures. The colors indicate the temperatures in the decade around 2000 as compared to average values from about 40 years earlier. Specifically, the colors compare average temperatures during the years 1995 through 2004 versus the averages from 1940 through 1980. The global averge temperature increased about 0.42° C during this time. Credits: Map image courtesy of Robert A. Rohde and the Global Warming Art project. Graph is original artwork by Windows to the Universe staff (Randy Russell) using data from NOAA. |
Use the popup menu in the upper left corner of the interactive below to select a map to view. Choices include contemporary global surface air temperature and sea surface temperature, changes in temperature by 2000, and four climate model projections for possible future climate in 2025 and 2095.
Compare maps side-by-side using the viewer below.